Kaggle-OpenProblem
# Kaggle-OpenProblem
# 数据集
# 数据集解释
evaluation_ids.csv
metadata.csv
sample_submission.csv
test_cite_inputs.h5
test_multi_inputs.h5
train_cite_inputs.h5
train_cite_targets.h5
train_multi_inputs.h5
train_multi_targets.h5
本次比赛有两个任务,一个是citeseq,一个是multiome,可以看成两个比赛
cite和multi分别对应citeseq和multiome
For the Multiome samples: given chromatin accessibility, predict gene expression. DNA->RNA
For the CITEseq samples: given gene expression, predict protein levels. RNA->Protein
0.743 for CITE and 0.257 for MULTI
# evaluation_ids.csv

# metadata.csv
描述了测量天数,捐赠者,细胞类型(不准确),测量技术

MasP = Mast Cell Progenitor
MkP = Megakaryocyte Progenitor
NeuP = Neutrophil Progenitor
MoP = Monocyte Progenitor
EryP = Erythrocyte Progenitor
HSC = Hematoploetic Stem Cell
BP = B-Cell Progenitor
# sample_submission.csv
和evaluation_ids.csv一一对应
| evaluation_id | sample_id |
|---|---|
 |  |
# train_cite_inputs.h5

Citeseq中每个细胞有22050个特征,且大部分为0。表格没有缺失值。
# train_cite_targets.h5

140列为已被dsb归一化的相同细胞的表面蛋白水平。
target 是 140 ,可以用140个机器学习器(lgbm xgb),也可以全部预测用cell做mse loss或pearson loss
Gene列的名称有蛋白质关系
Important_cols is the set of all features whose name matches the name of a target protein. If a gene is named 'ENSG00000114013_CD86', it should be related to a protein named 'CD86'. These features will be used for the model unchanged, that is, they don't undergo dimensionality reduction.
所有的140 column如下
CD含义: Cluster of Differentiation 分化簇
Cluster map绘制 (opens new window)

# train_multi_inputs.h5

每个细胞有22万个特征
# train_multi_targets.h5

每个细胞23418个目标
# 测试集
两个测试集,除了没有标签之外其他和train相同
- test_cite_inputs.h5
- test_multi_inputs.h5
# 汇总
综上所述
mutiome任务,输入维度22万,输出标签23418个
citeseq任务,输入维度2万,输出标签140个
数据量巨大
⭐在特征降维和数据加载上都具有挑战
# 模型&提交相关
# CV划分
kf.split(X, groups=meta.donor)
特征和天数也有关系,随着时间有固定方向的偏移

注意:ensemble要统一cv
# 模型训练-Pytorch
config = dict(
layers = [128, 128, 128],
...
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer_size_lst, add_final_activation=False):
super().__init__()
assert len(layer_size_lst) > 2
layer_lst = []
for i in range(len(layer_size_lst)-1):
sz1 = layer_size_lst[i]
sz2 = layer_size_lst[i+1]
layer_lst += [nn.Linear(sz1, sz2)]
if i != len(layer_size_lst)-2 or add_final_activation:
layer_lst += [nn.ReLU()]
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(*layer_lst)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
在Kaggle 16G GPU,13G RAM中,可以传入进来一个22万维的tensor稀疏向量torch.Size([512, 228942])
缺点:
只能使用max归一化;减去平均值,会破坏这里的tensorCSR稀疏性。操作受限。
# 模型训练-降维
- 人工特征+PCA/SVD降维+树模型/MLP
graph LR
A[人工特征] --> B[PCA/SVD/UMAP]
B --> C[树模型/ML模型/MLP]
A --> D[TensorCSR]
D --> C
2
3
4
5
- 其他降维方法
list_fast_methods = ['PCA','umap','FA', 'NMF','RandProj','RandTrees'] # 'ICA',
list_slow_methods = ['t-SNE','LLE','Modified LLE','Isomap','MDS','SE','LatDirAll','LTSA','Hessian LLE']
2
# Loss
| Pearson | MSE |
|---|---|
class NegativeCorrLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, preds, targets):
my = torch.mean(preds, dim=1)
my = torch.tile(torch.unsqueeze(my, dim=1), (1, targets.shape[1]))
ym = preds - my
r_num = torch.sum(torch.multiply(targets, ym), dim=1)
r_den = torch.sqrt(
torch.sum(torch.square(ym), dim=1) * float(targets.shape[-1])
)
r = torch.mean(r_num / r_den)
return -r
| def criterion(outputs, labels):
""" MSE Loss function"""
return nn.MSELoss()(outputs, labels) |
两个可以都尝试一下
# ensemble策略
Statement 1. Correlation loss is insensitive to linear transformations of predictions
Statement 2. Per-cell_id standardization helps to rescale base submissions
Under assumption that two base submissions are similar and demonstrate similar performance we could rescale them in the way that they become comparable and weighting in a regular way becomes adequate:

- Statement 3. Weighting coefficients don't have to add up to 1!
This is one of the benefit of the loss function that is agnostic to linear transformations. You don't have to weight base submissions as usual with . Any coefficients will do the job!
作者做了一个实验

| std前 | std后 |
|---|---|
| 0.92417836 | 0.94238122 |
# 比赛特点
本次比赛只需要提交submission.csv,也就是纯表格赛。人数会非常多。
训练时间无限,可无限融合
# 参考信息
In my case my out of folds CV for cite is 0.8882 and for multi is 0.6601 (opens new window),baseline&改进 训练出这个数大概就是对了
# 2021年冠军方案
# AE-JAE

在预训练阶段,JAE是用细胞注释信息(细胞类型、细胞周期阶段得分)可用的探索数据进行训练。在没有细胞注释信息的测试阶段,我们只用较小的学习率(微调)来最小化自动编码器的重建损失。
# AE-CLUE

# Novel team


# MY EDA
# 表格列名


DNA->RNA(1)
RNA(2)->Protein
RNA(1)和RNA(2)之间有特征重叠,但是细胞没有交集
https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000121410

# Citeseq训练结果
Citeseq best score: 0.893
# Multiome训练结果
multiome best score: 0.662
# Multiome列名顺序
graph LR
A(GL000194.1:114519-115365) --> B(GL000194.1)
A --> C(114519-115365)
B --> D("{name:GL000194.1,range:[114519-115365]}")
C --> D
2
3
4
5


multiom column列名全部为有序排列的,是否可以直接卷积?
https://lanceotron.molbiol.ox.ac.uk/projects/peak_search_basic/6243
graph BT
A("8 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
B("16 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
C("32 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
D("64 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
E("128 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
F("256 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
G("512 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
H("1024 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
I("2048 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
J("2048 channel 1*3,MaxPooling1D(3),ReLU")
A --> B
B <--> C
C --> D
D --> E
E --> F
F --> G
G --> H
H --> I
I --> J
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# CNN Results
| 名称 | 说明 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| v4-cnn | cnn 8~2048 channel | 0.6421 |
| base | baseline batch 512 | 0.6626 |
| v5-mlp | baseline batch 16 | 0.666 |
| v6-cnn | 8 kernel channel each layer , 8 layers | 0.647 |
- 问题
torch sparse中没有reshape方法
| 名称 | 说明 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| base | baseline batch 512 | 0.6626 |
| v6-cnn | 8 kernel channel each layer , 8 layers | 0.647 |
| v7-cnn | 16~32 channels | 0.65 |
| v8-cnn | 128 channel | 0.6508 |
| v10-cnn | BN,residual connection,48 channels | 0.6544 |
# 公开的NoteBook
# MSCI CITEseq Keras Quickstart + Dropout - LB 0.810
Solution for citeseq
Dimensionality reduction: To reduce the size of the 10.6 GByte input data, we project the 22050 features to a space with only 64 dimensions by applying a truncated SVD. To these 64 dimensions, we add 144 features whose names shows their importance.
结合了PCA和人工筛选特征的优势
- Hyperparameter tuning with KerasTuner: We tune the hyperparameters with KerasTuner BayesianOptimization.
- Cross-validation: Submitting unvalidated models and relying only on the public leaderboard is bad practice. The model in this notebook is fully cross-validated with a 3-fold GroupKFold.
泛化能力、模拟private set真实场景
- Use pearson loss directly
- The model is a sequential dense network with four hidden layers.
- Define two sets of features:
constant_cols is the set of all features which are constant in the train or test datset.
important_cols is the set of all features whose name matches the name of a target protein. If a gene is named 'ENSG00000114013_CD86', it should be related to a protein named 'CD86'.They don't undergo dimensionality reduction.
Finally ,we get 256 SVD features + 144 important features
但是根据这篇讨论帖子 (opens new window),important_cols 筛选的基因其实相关系数低

- 回归任务上的问题:Dropout
| dropout | without dropout |
|---|---|
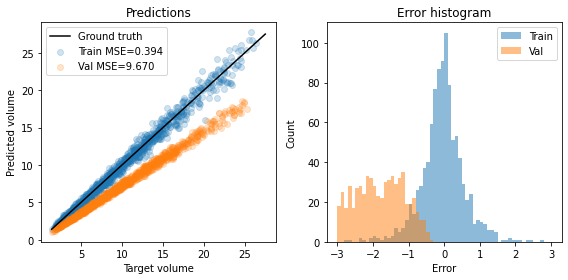 |  |
在训练期间使用dropout时,将对其输出进行放缩,以在dropout层之后保留其平均值。但是,variance尚未保留。因此,它仅仅获取了trainset的统计信息,因此在dropout时在valset时预测失效。
dropout仅仅适用于只有输出的相对大小很重要的任务,例如猫狗分类logits;输出Regression中代表绝对数值时,会推理时性能差。
# [🥈LB_T15| MSCI Multiome] CatBoostRegressor - LB 0.810
Solution for multiome
CatBoostRegressor
2 PCAs , 1 for input , 1 for target

- 优点
输入输出都用pca降维,节约模型训练需要的空间,减少模型训练难度
- 缺点
pca反向转换有损,且结果难以解释
# 🔬[Multi:.67;CITE:.89] PyTorch Swiss Army Knife🔬 - LB 0.809
TruncatedSVD is used to project raw features to 512 dimensional space.
Raw data is loaded to memory as sparse matrices and is lazily uncomressed and concatenated with cell_id features in the MSCIDatasetSparse class.
Optuna Hyperparameter Optimization
Random kfold split
MLP Model

# MSCI Multiome Torch Quickstart Submission - LB 0.808
Solution for multiome/citeseq
使用Pytorch Sparse Tensor
大幅减少内存压力,无需预先PCA降维
- MLP
graph LR
A["Input(228942)"] --> B["Linear(128)"]
B --> C["ReLU"]
C --> D["Linear(128)"]
D --> E["ReLU"]
E --> F["Linear(128)"]
F --> G["ReLU"]
G --> H["Linear(23418)"]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
模型简单有效
缺点
sparse tensor只能为二维,[batch,feature],仅适用于mlp。想使用其他方法,必须转换为dense tensor
# Fork of [MSCI Multiome] RandomSampling | Sp 6b182b - LB 0.804
Solution for Multiome
Pearson loss
Random KFold
KernelRidge/Tabnet Regression
pca inverse transform
# MSCI CITEseq Quickstart - LB 0.803
Dimensionality reduction . PCA->512 features
Domain knowledge: The column names of the data reveal which features are most important.
We fit 140 LightGBM models to the data (because there are 140 targets).
训练了140个学习器,因为单个模型不能适配所有任务;但对于multiome任务,训练2w个学习器不可行
- 3-fold GroupKFold
# CITEseq - RNA to Protein Encoder-Decoder NN - LB 0.798
PCA 降维
Encoder Decoder NN
AdamW optimizer with Cosine scheduler
可改进
尝试 rnn 、 cnn
尝试 attention mechanism
更改网络结构、添加新的特征
# 预处理 normalize Y to 1e6 (Multiome)


calculate predictions Y
calculate normalizer Z = sum(exp(Y))
renorm: Y_i -> Y_i + (log((1e6+22050 )/Z))
# Count nonzero genes - decrease daily
随着天数的增加,非0基因表达的数量减少
猜测是细胞增殖速度减慢



基因表达的sum和与基因表达的非0基因个数的相关系数0.996
# Tips on Dimensionality Reduction
- Handle Zeros
数据集包含是大量的零。甚至还有整个列仅由零组成
Here's a tip on how to remove them.
all_zero_columns = (X == 0).all(axis=0)
X = X[:,~all_zero_columns]
2
- ICA
独立的组件分析(ICA)发现哪些向量是数据的独立子元素。换句话说,PCA有助于压缩数据,ICA有助于分离数据。
Example code:
from sklearn.decomposition import FastICA
ica = FastICA(n_components=n)
X = ica.fit_transform(X)
2
3
- PCA
主成分分析(PCA)是一种线性降维,利用数据的奇异值分解将其投射到一个较低的维度空间。
Example code:
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=n)
X = pca.fit_transform(X)
2
3

但是PCA会破坏稀疏性,不支持稀疏向量
- t-SNE
T-SNE 是一种无监督的非线性降维和数据可视化分析技术,可以作为主成分分析的另一种替代方法.
Example code:
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
tsne = TSNE(n_components=n)
X = tsne.fit_transform(X)
2
3

- Ivis
IVIS有生物分子任务应用的前景。它使用Siamese神经网络来创建嵌入并降低尺寸的数量。预测它可能在此挑战中有良好的应用。
Example code:
from ivis import Ivis
model = Ivis(embedding_dims=dims, k=k, batch_size=bs, epochs=ep, n_trees=n_trees)
X = model.fit_transform(X)
2
3

# 单细胞数据分析软件包
几个用于单细胞数据分析的Python软件包:
# Pearson Correlations EDA
- Quick view
the individual correlations between a single target and a single input are rather small
10 Multiome inputs constantly equal to zero; 560 targets constantly equal to zeros.
Examples(一些重要的基因) :
For example
chr1:47180897-47181792seem to be a enhancer for 35% of targets, and an inhibitor for 11% of them.On the contrary,
chr2:28557270-28558187seem to be an inhibitor for 30% of targets and an enhancer for 11% of them.
- Sub groups
These approximate ratios of 30% / 10% of negative/positive correlations appear surprisingly often.
| Possibly there are two subgroups of highly correlated targets representing about 30% and 10% of all targets and that have a very similar response to the same inputs. |
# 关联规则

对于 inputs -> inputs / targets -> targets
则内部存在耦合
inputs -> targets / targets -> inputs
可提取为特征
Steps :
df=(df-df.mean())/df.std()(df>13)每列选择十几个,减少时间复杂度apriori(data, min_support=sup_thresh, min_confidence=conf_thresh)
其中sup_thresh,conf_thresh = 0.0005,0.5
# Summary
特征
降维
input pca降维,output pca降维
- 模型
Catboost、LGBM、Tabnet、Ridge、MLP、Encoder Decoder NN、SVR ; Tricks
- cv
Group kfold on donor
- 调参
keras tuner , optuna
# 集成Tricks
# 60种特征工程
# LR

- 当training loss大于一个阈值时,进行正常的梯度下降;当training loss低于阈值时,会反过来进行梯度上升,让training loss保持在一个阈值附近,让模型持续进行“random walk”
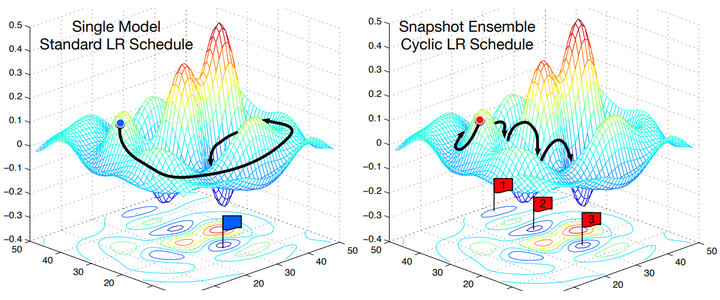
- 每隔一段时间重启学习率,这样在单位时间内能收敛到多个局部最小值,可以得到很多个模型做集成。
# 其他
几十、几百个模型的集成
调种子
HyperParam Tunner
torch & tf & jax